What to Eat Before a Workout - A Macronutrient Guide
SQUATWOLF

Summary
When starting out their fitness journeys, many beginners look into the best preworkout snack options. And for the newbies, deciding on what to eat before a workout can be quite tricky. This guide simplifies all about preworkout snacks so you know what to eat before a workout - along with their macronutrients.
- First, we will look into the basics of macronutrients, why they are important, and what role each plays.
- Then, we will look into why you need proper nutrition before a workout.
- At last, we look into what to eat before a workout and when.
What Are Macros?
There are three macronutrients found in your food which provide calories and energy: fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Each has a specific role towards providing you energy for your workouts.
However, you're supposed to consume each in different compositions, depending on your workout and the timing of consumption.
- Carbohydrates will have the biggest composition in your pre-workout snack. Carbs let your glycogen stores increase, preventing your body from going into a catabolic state.
- Fats have a bad name but they are also built up from the essential fatty acids such as Omega-3 and Omega-6. They provide you with concentrated energy, which is crucial for a workout.
- Protein is not very popular for a pre-workout meal but has a vital role to play in Muscle Protein Synthesis. Protein helps in increasing muscle anabolism.
| Macros | Carbs | Fats | Proteins |
| Composition | 45-65% | 20-35% | 10-35% |
| Types | Complex & Simple | Saturated, Unsaturated & Trans | Essential & Non-essential amino-acids* |
| Workout | For short & high intensity workouts | For longer & moderate-to-low workouts | Resistance & balance exercises |
| Calories per gram | 4 | 9 | 4 |
Need some light and low-calorie options? Try these 5 under-500 calorie vegetarian salad options!
Why Do You Need To Know Your Macros?

Keeping a check on nutrition can be very difficult. A simple way to understand them is knowing your macros.
- They are just three with a specific role to play.
- Every food is divided into macros.
- Understanding a few features will help you know a lot more about nutrition.
How to Track Your Macros Easily?
Smartphone applications such as Lifesum & MyFitnessPal will make tracking your macros super easy.
- Install one of the Fitness Apps. Check out the Top 5 Fitness Apps for Tracking.
- Enter your information.
- Your fitness goals and target weight.
- Start logging in whatever you eat (everyday).
- The app will tell you what macros you are consuming and what you need to achieve your goals.
5 Benefits of Pre-Workout Meal
Proper nutrition is equally important to lifting weights. Athletes and bodybuilders are focused on their diet as much as they are on their workouts.
Here is a list of reasons that will convince you even more why you should give equal or more importance to your diet before hitting the gym.
- More energy to complete your workout: Carbohydrates and glycogen are the main source of energy. They convert into energy faster than any other macros.
- Prevent your body from going into a catabolic state: Glycogen stores are first used up while exercising. When glycogen starts to deplete, your body uses your muscle energy which reduces the growth of muscles and recovery.
- Increases muscle anabolism: While a catabolic state extracts complex molecules into simpler ones, extracting energy, anabolism is exactly the opposite of converting simple molecules into synthesized complex ones. As a result, proper nutrition will give you more glycogen in the body, and allow protein muscle synthesis.
- Lower muscle soreness and fatigue: Lack of energy while working out can lead to muscle soreness and fatigue, just like an engine running out of fuel. Forcing yourself to work out without energy will be counterproductive and would start hurting your body.
- Maximize your performance: Ample energy won’t just let you complete your workout, but also let you perform at your best. Every athlete or performer needs to be at their best to grow themselves.
What to Eat Before a Workout & How Long Before?
Here we list some of the most popular foods you can eat before a workout. Some of them digest quicker than others so make sure you get your timing right.
2-3 Hours Before The Workout
Go for a complete meal 2-3 hours before a workout. Meal that has complex carbs and lean protein. There are various options you can go for with lots of mix and matches.
Here are a few of them:
- Eggs & Brown Bread
- Whole Grain Sandwich with Lean Meat & Salad
- Brown Rice & Lean Protein
- Sweet Potato, Chick Peas & Lean Meat
- Sweet Potato & Chicken
2 Hours Before The Workout
Porridge and Oatmeal are considered the ultimate pre-workout meals. A fruit smoothie is high in calories and fructose. Don’t mistake it with a meal but treat it as a great pre-workout dose.
- Fruit Smoothie
- Whole Grain Cereal & Milk
- Oatmeal with Almonds & Banana
- Sweet Potato Porridge
Less Than An Hour Before The Workout
If you are in a rush and need a quick boost before a workout you still have plenty of options. Dried Fruits are high in calories (energy) and can be consumed for a quick source of simple sugar. Greek yoghurt is a great source of proteins.
Whereas, power bars are full of nutrients including the dried fruits. Single fruits provide simple carbs that break down fast. Get a protein shake if you are lacking protein intake.
- Greek Yoghurt & Dried Fruit
- Nutrition, Protein or Power Bar
- Fruits: Banana, Apple with Peanut Butter
- Protein Shake
What Macro Composition Should I Keep?
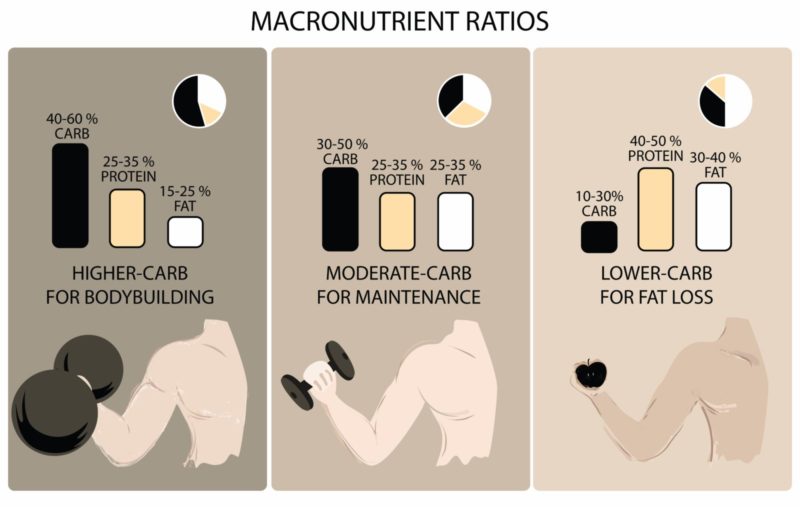 It depends on your fitness goals. The most common one to understand is whether to have a low-carb diet or high-carb diet. If you want to gain muscle, you should have a high-carb diet. (Combine with a hardcore workout) If you want to lose weight, you should have a low-carb diet. (Combine with cardio exercises)
It depends on your fitness goals. The most common one to understand is whether to have a low-carb diet or high-carb diet. If you want to gain muscle, you should have a high-carb diet. (Combine with a hardcore workout) If you want to lose weight, you should have a low-carb diet. (Combine with cardio exercises)
However, the best way to understand what your body requires is to download the Fitness Apps and know your macros.
Improve your digestion with these 5 healthy gluten-free snack options!
Supplemental Options for a Pre-Workout Meal
The use of supplements is common amongst athletes and bodybuilders. It is poised to improve performance, improve strength, and increase lean muscle mass. Some common Supplements are Creatine, Caffeine, BCAAs, and Beta-Alanine.
Depending on your goals, you can also look into Mass Gainers or Whey Protein!
Key Takeaways
Whether you're trying to lose weight or gain lean muscle, remember to create a nutrition plan that keeps you energized and satiated.
A hungry body leads to a tired mind - and to stay consistent with your fitness goals, it's important to fuel your body with nutritious options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good macronutrient ratio for weight loss?
For weight loss, finding the right balance of macronutrients can help you feel satisfied while eating fewer calories. Here's a good starting point:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of your total daily calories. Go for whole grains and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables to feel full longer.
- Proteins: 10-35% of total daily calories. Lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes can help maintain muscle while losing weight.
- Fats: 20-35% of daily calories, with a focus on healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Adjust these ratios based on your body's response and personal preferences. Remember, it's important to consume high quality macronutrients rather than just going for low-calorie options for weight loss. By consuming highly nutritious and satiating foods paired with an intense workout plan, you'll be on your way to weight loss.
What should my macros percentage be?
Generally, your macros percentages vary based on your fitness goals, activity levels and the food you consume. Here's a brief guideline to calculate your macros according to your goals:
For general health and maintenance:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65%
- Protein: 10-35%
- Fats: 20-35%
For weight loss (focusing on reducing body fat while maintaining muscle):
- Carbohydrates: 40-50%
- Protein: 30-40%
- Fats: 20-30%
For muscle gain or high-intensity athletes:
- Carbohydrates: 50-60%
- Protein: 25-35%
- Fats: 15-25%
This is just a basic guideline. You need to adjust your macros based on how your body looks and feels, your energy levels and what your fitness goals are. You can always get in touch with a health expert or a PT to set your goals.
What is the best macro ratio for building lean muscle?
For building lean muscle, you need to incorporate higher protein intake for muscle repair and growth, enough carbs for energy and recovery, and healthy fats for hormonal health. Here’s a suggested ratio:
- Protein: 25-35% - Essential for muscle repair and growth. Aim for high-quality sources like lean meats, fish, dairy, and plant-based proteins.
- Carbohydrates: 45-55% - Powers your workouts and helps with recovery. Focus on complex carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Fats: 20-30% - Supports hormone production and overall health. Include healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Adjust these ratios based on your body's response, workout intensity, and goals. For personalized advice, consider consulting with a sports nutritionist.
How do I calculate my macros for bulking?
To calculate your macros for bulking:
1. Find your calorie needs: Use an online calculator to get your daily calorie needs. Add 250 to 500 calories to that number for bulking.
2. Choose your macro ratio: A typical ratio is 40% carbs, 30% protein, and 30% fats.
3. Calculate your macros:
- Protein: Aim for 1.0 to 1.2 grams per pound of your body weight.
- Carbohydrates: Make up 40% of your total calories. They give you energy.
- Fats: Fill the remaining 30% of your calories. Fats are important for health.
4. Example: If you need 3000 calories a day to bulk,
- Protein: 30% of 3000 = 900 calories ÷ 4 (calories per gram) = 225 grams.
- Carbohydrates: 40% of 3000 = 1200 calories ÷ 4 = 300 grams.
- Fats: 30% of 3000 = 900 calories ÷ 9 (calories per gram) = 100 grams.
Adjust these numbers based on your progress and how your body responds.